Starting before the Lunar New Year in January the Chinese government’s heavy-handed measures fighting the coronavirus, including a lockdown on 60 million people in Hubei province and strict quarantine of hundreds of millions of people, have brought China’s economy to a near standstill.
In a sign of the situation is under control, China has stepped up efforts to ramp up production and to minimize the economic impacts caused by the coronavirus outbreak.
What is the progress on production resumption in China?
In the first week of March estimated production level outside Hubei province reached 60%-70%. As more areas are abolishing travel and transportation restrictions, production should be normalized by mid- to-late March.
Production resumption varies across regions, industries and enterprises. By region, majority of provinces on the Eastern coast have achieved a resumption rate of over 90%, while heavily-infected areas such as Hubei province still focuses on virus control.
By industry, financial and IT sectors have much higher reopening ratio, however basic materials sector is slow in restarting work. Over 90% of China’s State-Owned Enterprises (SOEs) have resumed production, but Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) still face difficulties to reach full-production.
What is the impact on China’s economy?
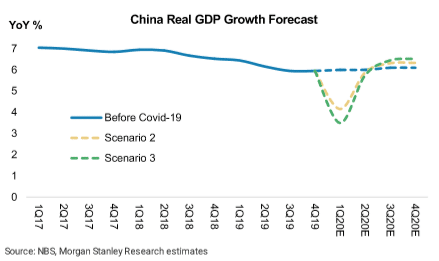
The disruption in production and consumption in January and February will lead to a slowdown in China’s economic growth in 1Q 2020.
This should be followed by a strong rebound in 2Q 2020 on quarter-on-quarter base. With gradual production normalization the Chinese economy is expected to revert to the pre-virus track toward the end of the year, with full-year growth rate reaching 5,7% in year-on-year term.
On the economic drivers, monetary and fiscal easing to boost growth is underway. Consumption could see a compensatory pick-up. The domestic and overseas inventory restocking after the production disruption is likely to support demand.
One man’s loss is another man’s gain. While the coronavirus outbreak caused economic downturns in the catering-, retail-sales- and tourism industry, it also triggered opportunities for the other industries, such as E-Commerce, online-learning and online-entertainment etc. “Less offline, more online; less human, more automation” is a strong trend across businesses.
Although the Chinese economy seems on its way of normalization, the clouds of uncertainly remains on the horizon. The duration and seriousness of the coronavirus outbreak outside China is highly unpredictable at this stage. Intervention by governments in different countries could cause reduction in extern demand.
After all the coronavirus is a one-off negative shock for the Chinese economy, but China’s long-term growth trends are intact.
Majority of provinces on the Eastern coast have achieved a recovery rate of over 90%
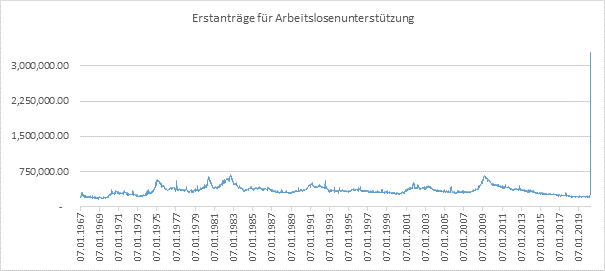
Slowdown in 1Q2020 and rebound in 2Q2020
Our dossier on coronavirus with analyses: https://blog.en.erste-am.com/dossier/coronavirus/
Legal note:
Prognoses are no reliable indicator for future performance.
Legal disclaimer
This document is an advertisement. Unless indicated otherwise, source: Erste Asset Management GmbH. The language of communication of the sales offices is German and the languages of communication of the Management Company also include English.
The prospectus for UCITS funds (including any amendments) is prepared and published in accordance with the provisions of the InvFG 2011 as amended. Information for Investors pursuant to § 21 AIFMG is prepared for the alternative investment funds (AIF) administered by Erste Asset Management GmbH pursuant to the provisions of the AIFMG in conjunction with the InvFG 2011.
The currently valid versions of the prospectus, the Information for Investors pursuant to § 21 AIFMG, and the key information document can be found on the website www.erste-am.com under “Mandatory publications” and can be obtained free of charge by interested investors at the offices of the Management Company and at the offices of the depositary bank. The exact date of the most recent publication of the prospectus, the languages in which the fund prospectus or the Information for Investors pursuant to Art 21 AIFMG and the key information document are available, and any other locations where the documents can be obtained are indicated on the website www.erste-am.com. A summary of the investor rights is available in German and English on the website www.erste-am.com/investor-rights and can also be obtained from the Management Company.
The Management Company can decide to suspend the provisions it has taken for the sale of unit certificates in other countries in accordance with the regulatory requirements.
Note: You are about to purchase a product that may be difficult to understand. We recommend that you read the indicated fund documents before making an investment decision. In addition to the locations listed above, you can obtain these documents free of charge at the offices of the referring Sparkassen bank and the offices of Erste Bank der oesterreichischen Sparkassen AG. You can also access these documents electronically at www.erste-am.com.
Our analyses and conclusions are general in nature and do not take into account the individual characteristics of our investors in terms of earnings, taxation, experience and knowledge, investment objective, financial position, capacity for loss, and risk tolerance. Past performance is not a reliable indicator of the future performance of a fund.
Please note: Investments in securities entail risks in addition to the opportunities presented here. The value of units and their earnings can rise and fall. Changes in exchange rates can also have a positive or negative effect on the value of an investment. For this reason, you may receive less than your originally invested amount when you redeem your units. Persons who are interested in purchasing units in investment funds are advised to read the current fund prospectus(es) and the Information for Investors pursuant to § 21 AIFMG, especially the risk notices they contain, before making an investment decision. If the fund currency is different than the investor’s home currency, changes in the relevant exchange rate can positively or negatively influence the value of the investment and the amount of the costs associated with the fund in the home currency.
We are not permitted to directly or indirectly offer, sell, transfer, or deliver this financial product to natural or legal persons whose place of residence or domicile is located in a country where this is legally prohibited. In this case, we may not provide any product information, either.
Please consult the corresponding information in the fund prospectus and the Information for Investors pursuant to § 21 AIFMG for restrictions on the sale of the fund to American or Russian citizens.
It is expressly noted that this communication does not provide any investment recommendations, but only expresses our current market assessment. Thus, this communication is not a substitute for investment advice.
This document does not represent a sales activity of the Management Company and therefore may not be construed as an offer for the purchase or sale of financial or investment instruments.
Erste Asset Management GmbH is affiliated with the Erste Bank and austrian Sparkassen banks.
Please also read the “Information about us and our securities services” published by your bank.

