Brinkmanship refers to playing with fire. Here, the parties involved threaten as credibly as possible to go to the edge of the abyss in order to enforce their own position. The aim is to persuade the opposing party to give in.
In the current case, the Democrats and Republicans in the US are using this strategy to negotiate the national budget. This is necessary because the beginning of June marks the point at which the US can no longer take on new debt. Raising the debt ceiling requires approval in both houses of the US Congress. If neither gives in, default, or technical bankruptcy, would be the result.
Centrists reach agreement on Debt Ceiling
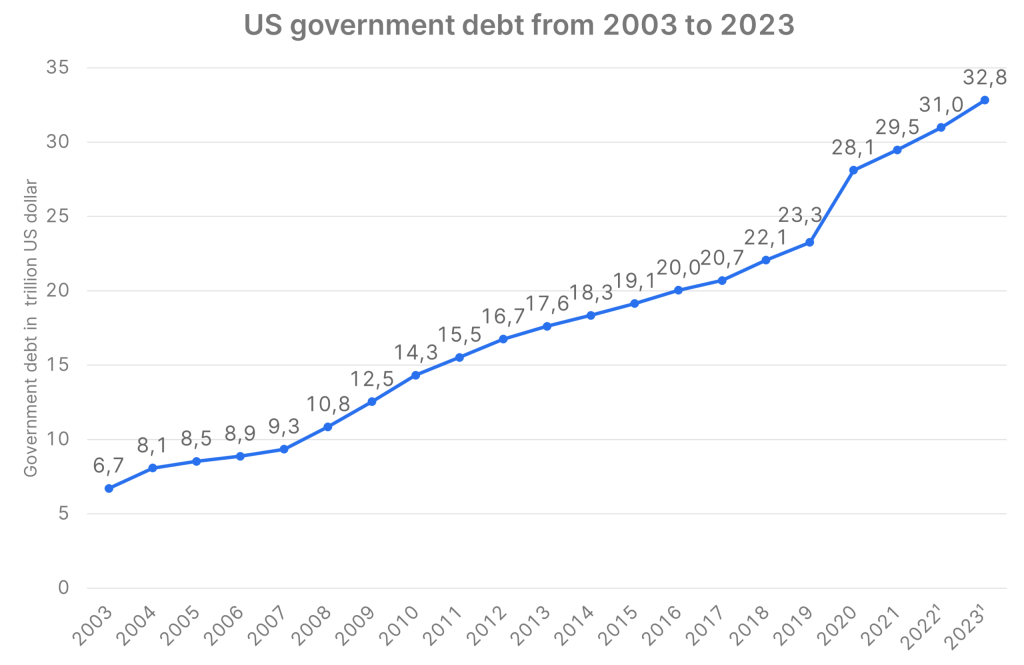
Democratic and Republican representatives have now reached a compromise. President Joe Biden (a Democrat) and Speaker of the House Kevin McCarthy (a Republican) have agreed to suspend the debt ceiling of 31,400 billion US dollar for two years, until 2025.
Deferral
Those government expenditures, the non-discretionary ones, are not to increase in fiscal year 2024 and are to increase by only one percent in fiscal year 2025. These restrictions do not apply to:
- defense
- social security
- state pensions
- and health (Medicare).
At the same time, eligibility criteria for poverty programs are tightened. The system of tax credits in the Inflation Reduction Act is not changed. Instead, criteria for the environmental assessment of infrastructure projects will be relaxed. According to preliminary estimates, GDP will be reduced only slightly (by several tenths of a percentage point) by the announced reduction in government spending compared with the situation without restrictions.
Residual risk remains
Both houses of Congress must approve the agreement. The House of Representatives will vote as early as next Wednesday. The Senate follows a few days after that. Because the polarization of the parties has increased, however, there is still a residual risk of non-agreement. The hardliners could therefore still overturn the centrists’ agreement.
Possible consequences of technical bankruptcy
A technical bankruptcy of the USA would lead to a massive increase in uncertainty on the financial market. This is because the yields on US government bonds act as the most important reference for many financial instruments. In addition, a US default would likely diminish confidence in the world’s most important reserve currency. Events would also likely dampen business and consumer sentiment. The likelihood of a recession would again increase.
Less liquidity on the market
The significantly reduced residual risk of a technical bankruptcy of the USA is positive for the financial markets. However, the effect is only short-term in nature. The lower growth in government spending will slightly dampen economic growth. In addition, the US Treasury will massively increase government bond issuance activity in the coming weeks. The Treasury’s account at the Federal Reserve has shrunk since May 2022 from just under $1,000 billion to currently only around $40 billion. However, the Ministry of Finance’s medium-term target is just under 600 billion. The additional issuance volume of over 500 billion will remove liquidity from the market. The effect is similar to a sale of government bonds by the central bank (quantitative tightening).
Conclusion
The agreement in the dispute over the US debt ceiling, subject to approval in the House of Representatives and Congress, is positive for financial markets. However, uncertainty about the extent of the reduced liquidity in the markets is likely to be a major market theme in the coming weeks.
In addition, the stale aftertaste remains that the financial markets will also have to deal with the effects of increasing political polarization, which may extend to political dysfunction.
For a glossary of technical terms, please visit this link: Fund Glossary | Erste Asset Management
Legal note:
Prognoses are no reliable indicator for future performance.
Legal disclaimer
This document is an advertisement. Unless indicated otherwise, source: Erste Asset Management GmbH. The language of communication of the sales offices is German and the languages of communication of the Management Company also include English.
The prospectus for UCITS funds (including any amendments) is prepared and published in accordance with the provisions of the InvFG 2011 as amended. Information for Investors pursuant to § 21 AIFMG is prepared for the alternative investment funds (AIF) administered by Erste Asset Management GmbH pursuant to the provisions of the AIFMG in conjunction with the InvFG 2011.
The currently valid versions of the prospectus, the Information for Investors pursuant to § 21 AIFMG, and the key information document can be found on the website www.erste-am.com under “Mandatory publications” and can be obtained free of charge by interested investors at the offices of the Management Company and at the offices of the depositary bank. The exact date of the most recent publication of the prospectus, the languages in which the fund prospectus or the Information for Investors pursuant to Art 21 AIFMG and the key information document are available, and any other locations where the documents can be obtained are indicated on the website www.erste-am.com. A summary of the investor rights is available in German and English on the website www.erste-am.com/investor-rights and can also be obtained from the Management Company.
The Management Company can decide to suspend the provisions it has taken for the sale of unit certificates in other countries in accordance with the regulatory requirements.
Note: You are about to purchase a product that may be difficult to understand. We recommend that you read the indicated fund documents before making an investment decision. In addition to the locations listed above, you can obtain these documents free of charge at the offices of the referring Sparkassen bank and the offices of Erste Bank der oesterreichischen Sparkassen AG. You can also access these documents electronically at www.erste-am.com.
Our analyses and conclusions are general in nature and do not take into account the individual characteristics of our investors in terms of earnings, taxation, experience and knowledge, investment objective, financial position, capacity for loss, and risk tolerance. Past performance is not a reliable indicator of the future performance of a fund.
Please note: Investments in securities entail risks in addition to the opportunities presented here. The value of units and their earnings can rise and fall. Changes in exchange rates can also have a positive or negative effect on the value of an investment. For this reason, you may receive less than your originally invested amount when you redeem your units. Persons who are interested in purchasing units in investment funds are advised to read the current fund prospectus(es) and the Information for Investors pursuant to § 21 AIFMG, especially the risk notices they contain, before making an investment decision. If the fund currency is different than the investor’s home currency, changes in the relevant exchange rate can positively or negatively influence the value of the investment and the amount of the costs associated with the fund in the home currency.
We are not permitted to directly or indirectly offer, sell, transfer, or deliver this financial product to natural or legal persons whose place of residence or domicile is located in a country where this is legally prohibited. In this case, we may not provide any product information, either.
Please consult the corresponding information in the fund prospectus and the Information for Investors pursuant to § 21 AIFMG for restrictions on the sale of the fund to American or Russian citizens.
It is expressly noted that this communication does not provide any investment recommendations, but only expresses our current market assessment. Thus, this communication is not a substitute for investment advice.
This document does not represent a sales activity of the Management Company and therefore may not be construed as an offer for the purchase or sale of financial or investment instruments.
Erste Asset Management GmbH is affiliated with the Erste Bank and austrian Sparkassen banks.
Please also read the “Information about us and our securities services” published by your bank.