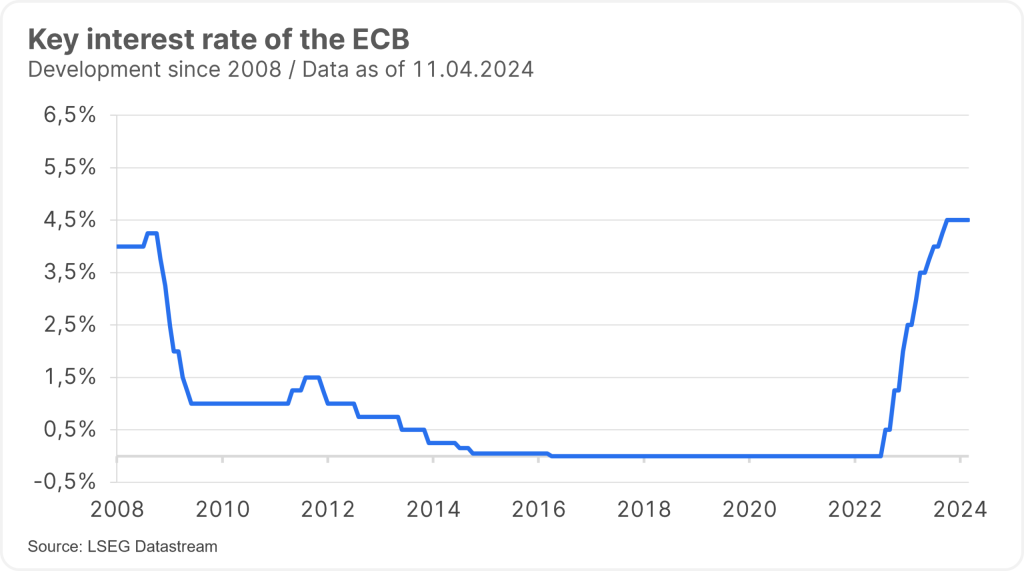
The key interest rate has a significant influence on how much interest you receive on your savings account or how much you have to pay when you take out a loan. The key interest rate of the European Central Bank (ECB) is currently 4.50% – but this could change at the ECB’s interest rate meetings in Frankfurt in the coming months.
The market is expecting key interest rates to be lowered this year after inflationary pressure has gradually eased in recent months. In this article, we discuss the role of the key interest rate and which interest rates are relevant.
👉 What you will read in this article
What role does the ECB’s key interest rate play?
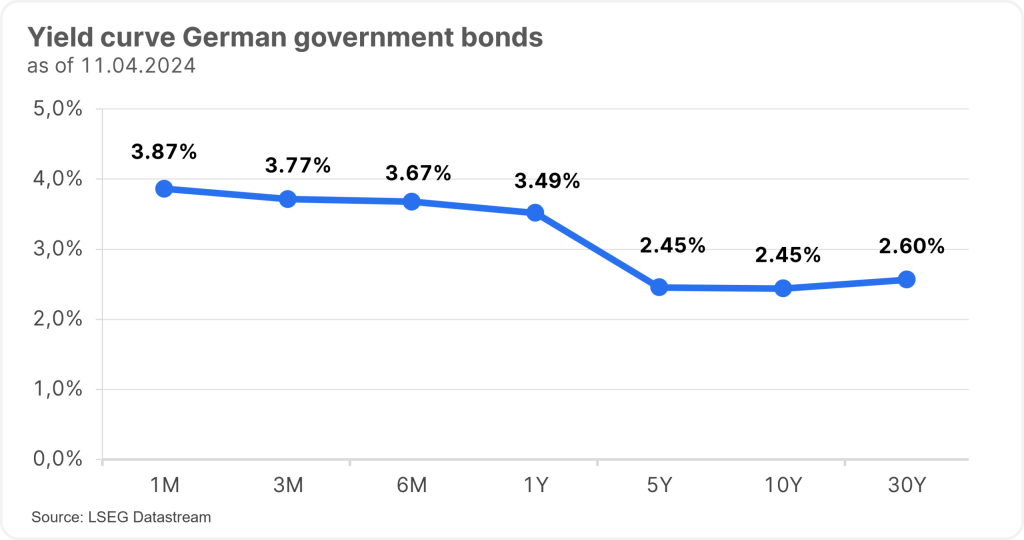
Key interest rates particularly influence the interest rate landscape at the short end, the so-called money market, and therefore maturities of up to a maximum of one year. This means that the central banks control the interest rate level at the short end with their interest rate policy. For example, the yield curve of German government bonds, which had been yielding negative returns for a long time, turned positive as a result of the most recent interest rate hikes by the central bank.
Interest rates (also known as “yields”) for long maturities are calculated on the capital market. When calculating “yields”, the current daily prices of government bonds, for example, and the interest payments on these bonds (“coupons”) are taken into account. This is why the interest payments (“coupons”) on bonds differ from the yields, as the prices and therefore the yields of bonds change daily, even by the second, in line with the new interest rate expectations of market participants.
Market participants analyze which interest rate decisions can be expected from the central bank and act accordingly. They are mainly guided by inflation trends and the economic picture. In recent years, central banks themselves have also acted as market participants in longer-term bonds by buying government and corporate bonds. This is part of the monetary policy instruments that a central bank has at its disposal.
So, what is THE key interest rate?
Strictly speaking, there are several key ECB interest rates. As a rule, the key interest rate is the interest rate at which commercial banks can borrow money from the ECB. This interest rate is also known as the main refinancing rate.
The Oesterreichische Nationalbank defines the key interest rate as follows: Short-term interest rate whose change influences other interest rates. The key interest rate is primarily defined as interest rates that can be set by a central bank as part of its monetary policy measures.
What are the European Central Bank’s interest rates?
| ECB interest rate | Explanation | Current level (as of 11 April 2024) |
| Deposit rate | Interest rate at which commercial banks can deposit their money with the ECB at very short notice (overnight) | 4.00% |
| Main refinancing rate (key interest rate) | Interest rate at which commercial banks can borrow money from the ECB for one week | 4.50% |
| Marginal rate | Interest rate at which commercial banks can borrow money from the ECB at short notice (“overnight”) | 4.75% |
How does the key interest rate affect savings account interest rates?
If the central bank raises the key interest rate, the interest rate on money that is newly saved, such as on a savings account, normally also increases. The key interest rate thus influences savings account interest rates.
🔎 Background
The key interest rate affects the so-called deposit rate. At this interest rate, banking institutions can deposit funds with the central bank at very short notice (overnight). Savers can orientate themselves on this deposit rate, which is significantly lower than the key interest rate, or main financing rate.
What drives the level of interest rates on savings books?
The basis is the deposit interest rate set by the European Central Bank for commercial banks. In addition, the savings account interest rate depends on whether a commitment period has been agreed or the amount can be withdrawn daily. The creditworthiness of the bank, the customers and the competition also play a role.
Worth knowing
There can be no negative interest rates on savings books. However, this is no longer an issue anyway, now that the ECB has raised interest rates. There is also a protective shield for savings books: the deposit guarantee scheme protects the savers. Savings and current account deposits are protected for up to EUR 100,000 per customer and bank.
How does the key interest rate affect the interest rate on loans?
The key interest rate affects the interest rate on loans via the refinancing rate if you have taken out a variable-rate loan. A variable-rate loan is based on the interest rates at the short end, for example the three-month money market rate. This money market rate fluctuates around the key interest rate, or refinancing rate. If you have a fixed-rate loan, the key interest rate does not affect it.
Conclusion
The most important key interest rate of the European Central Bank is the main refinancing rate. If this rate rises, it means that credit institutions are incurring higher costs for borrowing money from the central bank. Credit institutions take interest rates and their changes into account when concluding new contracts. Due to competition, banks react to different degrees and at different speeds. For savers, rising key interest rates mean that they can expect a higher interest rate for new funds.
More articles on the topic of financial knowledge 👇
No Posts Found
For a glossary of technical terms, please visit this link: Fund Glossary | Erste Asset Management
Legal note:
Prognoses are no reliable indicator for future performance.
Legal disclaimer
This document is an advertisement. Unless indicated otherwise, source: Erste Asset Management GmbH. The language of communication of the sales offices is German and the languages of communication of the Management Company also include English.
The prospectus for UCITS funds (including any amendments) is prepared and published in accordance with the provisions of the InvFG 2011 as amended. Information for Investors pursuant to § 21 AIFMG is prepared for the alternative investment funds (AIF) administered by Erste Asset Management GmbH pursuant to the provisions of the AIFMG in conjunction with the InvFG 2011.
The currently valid versions of the prospectus, the Information for Investors pursuant to § 21 AIFMG, and the key information document can be found on the website www.erste-am.com under “Mandatory publications” and can be obtained free of charge by interested investors at the offices of the Management Company and at the offices of the depositary bank. The exact date of the most recent publication of the prospectus, the languages in which the fund prospectus or the Information for Investors pursuant to Art 21 AIFMG and the key information document are available, and any other locations where the documents can be obtained are indicated on the website www.erste-am.com. A summary of the investor rights is available in German and English on the website www.erste-am.com/investor-rights and can also be obtained from the Management Company.
The Management Company can decide to suspend the provisions it has taken for the sale of unit certificates in other countries in accordance with the regulatory requirements.
Note: You are about to purchase a product that may be difficult to understand. We recommend that you read the indicated fund documents before making an investment decision. In addition to the locations listed above, you can obtain these documents free of charge at the offices of the referring Sparkassen bank and the offices of Erste Bank der oesterreichischen Sparkassen AG. You can also access these documents electronically at www.erste-am.com.
Our analyses and conclusions are general in nature and do not take into account the individual characteristics of our investors in terms of earnings, taxation, experience and knowledge, investment objective, financial position, capacity for loss, and risk tolerance. Past performance is not a reliable indicator of the future performance of a fund.
Please note: Investments in securities entail risks in addition to the opportunities presented here. The value of units and their earnings can rise and fall. Changes in exchange rates can also have a positive or negative effect on the value of an investment. For this reason, you may receive less than your originally invested amount when you redeem your units. Persons who are interested in purchasing units in investment funds are advised to read the current fund prospectus(es) and the Information for Investors pursuant to § 21 AIFMG, especially the risk notices they contain, before making an investment decision. If the fund currency is different than the investor’s home currency, changes in the relevant exchange rate can positively or negatively influence the value of the investment and the amount of the costs associated with the fund in the home currency.
We are not permitted to directly or indirectly offer, sell, transfer, or deliver this financial product to natural or legal persons whose place of residence or domicile is located in a country where this is legally prohibited. In this case, we may not provide any product information, either.
Please consult the corresponding information in the fund prospectus and the Information for Investors pursuant to § 21 AIFMG for restrictions on the sale of the fund to American or Russian citizens.
It is expressly noted that this communication does not provide any investment recommendations, but only expresses our current market assessment. Thus, this communication is not a substitute for investment advice.
This document does not represent a sales activity of the Management Company and therefore may not be construed as an offer for the purchase or sale of financial or investment instruments.
Erste Asset Management GmbH is affiliated with the Erste Bank and austrian Sparkassen banks.
Please also read the “Information about us and our securities services” published by your bank.